Educational Context
The educational context is a State Primary School in Brisbane with approximately 550 students. It is in a mid to high socio-economic area. In recent years, a vision for e-learning has been communicated by the school’s administration and is in the beginning stages of implementation. An ICT levy was introduced to purchase hardware and software for student use in classrooms. 90% of parents paid the levy in 2016, showing a willingness for their children to engage in the use of digital technologies.
Learner Profile
The students at the school are generally active and willing participants in school life. The school performs well in National Assessment Programs of Literacy and Numeracy (NAPLAN). Almost all students have access to digital devices and the Internet at home. The majority of students are English speaking. A special education unit is attached to the school and supports a number of special needs students, both with learning difficulty and physical impairment.
Learning Space
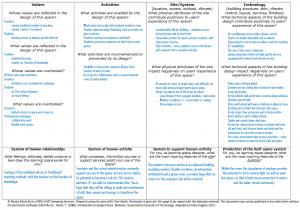
The learning space being evaluated is a computer laboratory, known as the ‘Learning Technology Centre’ (LTC), which sits within the school’s library. An evaluation of the LTC, considered ‘who and what is valued here’. This process was guided by using a VAST heuristic framework, adapted by Burns (2003) from the work of Heath (1989).
The tour of the LTC has revealed an incongruity between the school’s vision for learning and the functionality of the space.
Values
In its current form, the space values traditional teaching methods, with students adopting a passive role in the learning process. The value of contemporary pedagogy is overshadowed, despite the inclusion of digital tools for learning.
Activities
The activities that are enabled in this space are limited to students sitting in rows facing the front. The design of the space limits collaboration between students.
Site/System
The location of the site in the library, provides access to students at various times throughout the day. The location of the library at the top of the school (which is on a hill) makes access difficult during adverse weather conditions.
Technology
The inclusion of high quality laptop computers, which are equipped with network and Internet access contribute positively to users’ experience of this space. The data projector and screen provide opportunities for direct instruction to the group. There are several issues in relation to skin, layout, services and finishes that have a negative impact. These include: dull paintwork and broken and outdated fittings; large, heavy furniture in a fixed position (in rows); cables and cords cluttering desktop space; poor acoustics, resulting in a very noisy environment.
Learning Space Design Problem
Building design challenges, lack of aesthetic appeal and issues of physical inclusivity are all problems in this space. However, the main problem in relation to the educational context of the site is its lack of flexibility.
In its current embodiment, the LTC in unable to support 21st learners and the development of 21st century skills, such as creativity, communication and collaboration.
References
Heath, T. 1989. What do designers do? In Introduction to design theory. Brisbane: Queensland University of Technology.